Types/breast/surgery-choices
Contents
Surgery Choices for Women with DCIS or Breast Cancer
Are You Facing a Decision about Surgery for DCIS or Breast Cancer?
Do you have ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or breast cancer that can be removed with surgery? If so, you may be able to choose which type of breast surgery to have. Often, your choice is between breast-sparing surgery (surgery that takes out the cancer and leaves most of the breast) and a mastectomy (surgery that removes the whole breast).
Once you are diagnosed, treatment will usually not begin right away. There should be enough time for you to meet with breast cancer surgeons, learn the facts about your surgery choices, and think about what is important to you. Learning all you can will help you make a choice you can feel good about.
Talk with Your Doctor
Talk with a breast cancer surgeon about your choices. Find out:
- what happens during surgery
- the types of problems that sometimes occur
- any treatment you might need after surgery
Be sure to ask a lot of questions and learn as much as you can. You may also wish to talk with family members, friends, or others who have had surgery.
Get a Second Opinion
After talking with a surgeon, think about getting a second opinion. A second opinion means getting the advice of another surgeon. This surgeon might tell you about other treatment options. Or, he or she may agree with the advice you got from the first doctor.
Some people worry about hurting their surgeon’s feelings if they get a second opinion. But, it is very common and good surgeons don’t mind. Also, some insurance companies require it. It is better to get a second opinion than worry that you made the wrong choice.
If you think you might have a mastectomy, this is also a good time to learn about breast reconstruction. Think about meeting with a reconstructive plastic surgeon to learn about this surgery and if it seems like a good option for you.
Check with Your Insurance Company
Each insurance plan is different. Knowing how much your plan will pay for each type of surgery, including reconstruction, special bras, prostheses, and other needed treatments can help you decide which surgery is best for you.
Learn about the Types of Breast Surgery
Most women with DCIS or breast cancer that can be treated with surgery have three surgery choices.
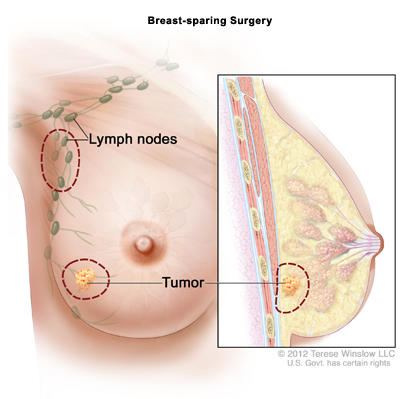
Breast-Sparing Surgery, Followed by Radiation Therapy
Breast-sparing surgery means the surgeon removes only the DCIS or cancer and some normal tissue around it. If you have cancer, the surgeon will also remove one or more lymph nodes from under your arm. Breast-sparing surgery usually keeps your breast looking much like it did before surgery. Other words for breast-sparing surgery include:
- Lumpectomy
- Partial mastectomy
- Breast-conserving surgery
- Segmental mastectomy
After breast-sparing surgery, most women also receive radiation therapy. The main goal of this treatment is to keep cancer from coming back in the same breast. Some women will also need chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and/or targeted therapy.
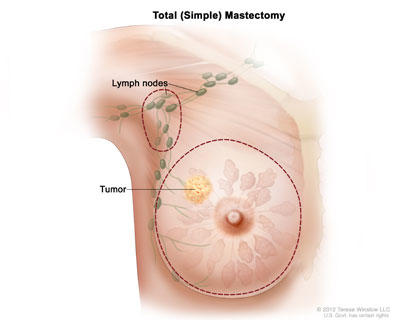
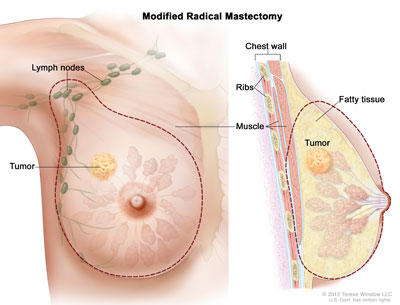
Mastectomy
In a mastectomy, the surgeon removes the whole breast that contains the DCIS or cancer. There are two main types of mastectomy. They are:
- Total mastectomy. The surgeon removes your whole breast. Sometimes, the surgeon also takes out one or more of the lymph nodes under your arm. Also called simple mastectomy.
- Modified radical mastectomy. The surgeon removes your whole breast, many of the lymph nodes under your arm, and the lining over your chest muscles.
Some women will also need radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and/or targeted therapy.
If you have a mastectomy, you may choose to wear a prosthesis (breast-like form) in your bra or have breast reconstruction surgery.
Mastectomy with Breast Reconstruction Surgery
You can have breast reconstruction at the same time as the mastectomy, or anytime after. This type of surgery is done by a plastic surgeon with experience in reconstruction surgery. The surgeon uses an implant or tissue from another part of your body to create a breast-like shape that replaces the breast that was removed. The surgeon may also make the form of a nipple and add a tattoo that looks like the areola (the dark area around your nipple).
There are two main types of breast reconstruction surgery:
Breast Implant
Breast reconstruction with an implant is often done in steps. The first step is called tissue expansion. This is when the plastic surgeon places a balloon expander under the chest muscle. Over many weeks, saline (salt water) will be added to the expander to stretch the chest muscle and the skin on top of it. This process makes a pocket for the implant.
Once the pocket is the correct size, the surgeon will remove the expander and place an implant (filled with saline or silicone gel) into the pocket. This creates a new breast-like shape. Although this shape looks like a breast, you will not have the same feeling in it because nerves were cut during your mastectomy.
Breast implants do not last a lifetime. If you choose to have an implant, chances are you will need more surgery later on to remove or replace it. Implants can cause problems such as breast hardness, pain, and infection. The implant may also break, move, or shift. These problems can happen soon after surgery or years later.
Tissue Flap
In tissue flap surgery, a reconstructive plastic surgeon builds a new breast-like shape from muscle, fat, and skin taken from other parts of your body (usually your belly, back, or buttock). This new breast-like shape should last the rest of your life. Women who are very thin or obese, smoke, or have serious health problems often cannot have tissue flap surgery.
Healing after tissue flap surgery often takes longer than healing after breast implant surgery. You may have other problems, as well. For example, if you have a muscle removed, you might lose strength in the area from which it was taken. Or, you may get an infection or have trouble healing. Tissue flap surgery is best done by a reconstructive plastic surgeon who has special training in this type of surgery and has done it many times before.
Enable comment auto-refresher