Types/liver/patient/child-liver-treatment-pdq
Childhood Liver Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version
General Information About Childhood Liver Cancer
KEY POINTS
- Childhood liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver.
- There are different types of childhood liver cancer.
- Certain diseases and conditions can increase the risk of childhood liver cancer.
- Signs and symptoms of childhood liver cancer include a lump or pain in the abdomen.
- Tests that examine the liver and the blood are used to detect (find) and diagnose childhood liver cancer and find out whether the cancer has spread.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Childhood liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver.
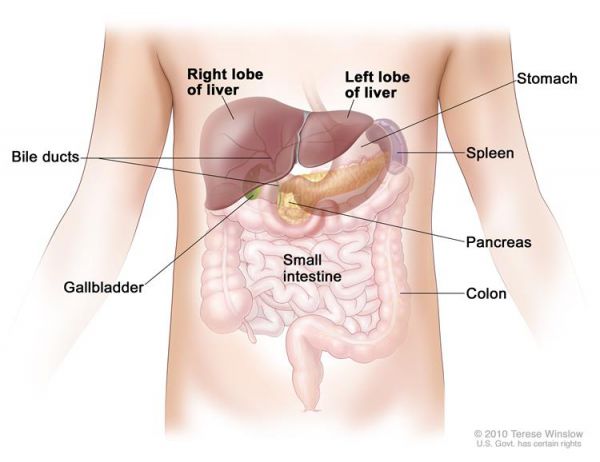
The liver is one of the largest organs in the body. It has two lobes and fills the upper right side of the abdomen inside the rib cage. Three of the many important functions of the liver are:
- To filter harmful substances from the blood so they can be passed from the body in stools and urine.
- To make bile to help digest fats from food.
- To store glycogen (sugar), which the body uses for energy.
Liver cancer is rare in children and adolescents.
There are different types of childhood liver cancer.
There are two main types of childhood liver cancer:
- Hepatoblastoma: Hepatoblastoma is the most common type of childhood liver cancer. It usually affects children younger than 3 years of age.
In hepatoblastoma, the histology (how the cancer cells look under a microscope) affects the way the cancer is treated. The histology for hepatoblastoma may be one of the following:
- Well-differentiated fetal (pure fetal) histology.
- Small cell undifferentiated histology.
- Non–well-differentiated fetal histology, non-small cell undifferentiated histology.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma: Hepatocellular carcinoma usually affects older children and adolescents. It is more common in areas of Asia that have high rates of hepatitis B infection than in the U.S.
Other less common types of childhood liver cancer include the following:
- Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma of the liver: This type of liver cancer usually occurs in children between 5 and 10 years of age. It often spreads all through the liver and/or to the lungs.
- Infantile choriocarcinoma of the liver: This is a very rare tumor that starts in the placenta and spreads to the fetus. The tumor is usually found during the first few months of life. Also, the mother of the child may be diagnosed with choriocarcinoma. Choriocarcinoma is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease. See the PDQ summary on Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment for more information on the treatment of choriocarcinoma for the mother of the child.
vVascular liver tumors: These tumors form in the liver from cells that make blood vessels or lymph vessels. Vascular liver tumors may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). See the PDQ summary on Childhood Vascular Tumors Treatment for more information on vascular liver tumors.
This summary is about the treatment of primary liver cancer (cancer that begins in the liver). Treatment of metastatic liver cancer, which is cancer that begins in other parts of the body and spreads to the liver, is not discussed in this summary.
Primary liver cancer can occur in both adults and children. However, treatment for children is different from treatment for adults. See the PDQ summary on Adult Primary Liver Cancer Treatment for more information on the treatment of adults.